What is Zero Trust - for executives
On a brief high-level, Zero Trust can be defined as follows:
Zero Trust is a new way of connectivity design. Since the mid 2000s, new business models start to gain traction. Software, Platform and Infrastructure as a Service become common. — How to connect them all?
Companies subscribe to Third-Party operated services and extend their supply-chain. Zero Trust is a way to define perimeters and connections. Not only based on Firewalls, but also based on logics.
From the CISA (Cybersecurity Infrastructure and Security Agency, USA) Zero Trust Maturity Model (April 2023, PDF)
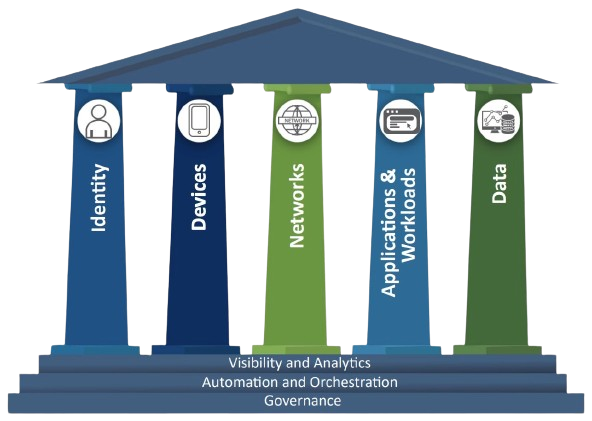
What are these new perimeter logics?
Identity
Devices
Applications
Data
Network
What Zero Trust is not: an airtight security concept, intended only for high-security environments.
What are the relevant use cases?
Faster time to solution in Information Security and Corporate IT:
Reduced process overhead for Remote Work, incl. entry and exit process management
Mergers and acquisitions may require tighter data control
Unified access to modern productivity applications
Simplified management of compliance in distributed organizations with branch offices and mobile work
Supply chain security management requirements become possible to implement
Higher resilience against disruptions
With Zero Trust, you can simplify your Enterprise Security Architecture and reduce the efforts in Information Security, Compliance and Corporate IT.
What are the key problems with Zero Trust
Sadly, you can also cause adverse effects with Zero Trust:
Many Zero Trust vendors misrepresent their solutions
Zero Trust implementations and service need to be robust
Network and Security Architecture may need to get redesigned
If you want to learn how to avoid these, check out this blog more regularly in the future.